

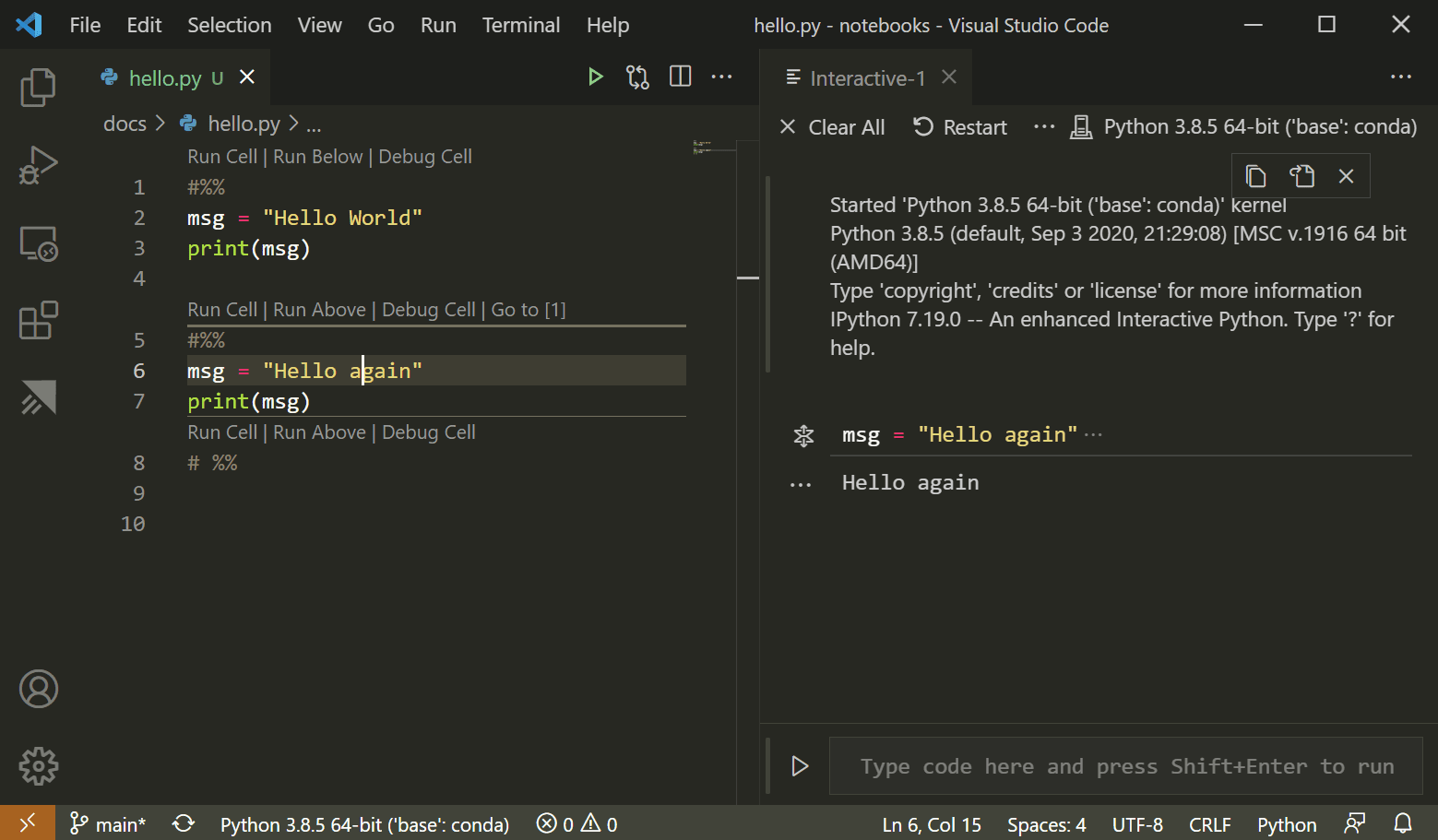
If you do not pass any folder name as the command line input arguments when you invoke list_file.py, it will list the files and directories’ names in the current directory. When you run this python script file in jupyter notebook, it will print out all the files and directories’ names in the folder which you pass to it as a command-line input argument.
#Python jupyter notebook to py code
Below ipython code will create a python script file with name list_file.py. Add the first line cell and input below source code.Click file InvokePythonScript.ipynb to edit it.( There are also 2 python script files list_file.py and list_file_path.py which we will introduce later. Create a jupyter notebook file with the name InvokePythonScript.ipynb.

Invoke Python Script File From Jupyter Notebook. Figure ( data = data, layout = layout ) py. Surface ( x = x, y = y, z = z ) data = layout = go. cos ( tGrid ) # z = r*cos(t) surface = go. sin ( tGrid ) # y = r*sin(s)*sin(t) z = r * np.
sin ( tGrid ) # x = r*cos(s)*sin(t) y = r * np. sin ( 7 * sGrid + 5 * tGrid ) # r = 2 + sin(7s+5t) x = r * np. Import chart_otly as py import aph_objects as go import numpy as np s = np. iplot ( fig, filename = 'jupyter-Nuclear Waste Sites on American Campuses' ) Layout ( title = 'Nuclear Waste Sites on Campus', autosize = True, hovermode = 'closest', showlegend = False, mapbox = dict ( accesstoken = mapbox_access_token, bearing = 0, center = dict ( lat = 38, lon =- 94 ), pitch = 0, zoom = 3, style = 'light' ), ) fig = dict ( data = data, layout = layout ) py. read_csv ( ' %20o n%20American%20Campuses.csv' ) site_lat = df. Import chart_otly as py import aph_objects as go import pandas as pd # mapbox_access_token = 'ADD YOUR TOKEN HERE' df = pd. See examples of statistic, scientific, 3D charts, and more here.
#Python jupyter notebook to py install
When installing packages in Jupyter, you either need to install the package in your actual shell, or run the ! prefix, e.g.: !pip install packagename Skip down to the for more information on using IRkernel with Jupyter notebooks and graphing examples. You can also use Jupyter notebooks to execute R code. The bulk of this tutorial discusses executing python code in Jupyter notebooks.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
